Iron-modified activated carbon enhanced Anammox-n-DAMO progress in granular sludge: Performance and microbial mechanism. #anammox #nitrogen #BNR #wastewater https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0011916424011937
Recent searches
Search options
#nitrogen
Iron-modified activated carbon enhanced Anammox-n-DAMO progress in granular sludge: Performance and microbial mechanism. #anammox #nitrogen #BNR #wastewater https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0011916424011937
Distinct assembly processes and interspecies interactions between anammox bacteria and co-occurring species across anammox granules. #anammox #ammonia #NH3 #bacteria #wastewater #nitrogen #BNR https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301479725014598
Distinct assembly processes and interspecies interactions between anammox bacteria and co-occurring species across anammox granules. #anammox #ammonia #NH3 #bacteria #wastewater #nitrogen #BNR https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301479725014598
Influence of long-term anthropogenic nitrogen input and its legacy on riverine output. #water #pollution #nitrogen #anthropogenic #river https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-00261-6
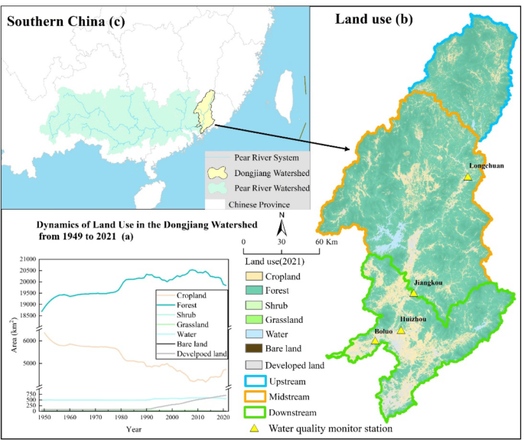
Influence of long-term anthropogenic nitrogen input and its legacy on riverine output. #water #pollution #nitrogen #anthropogenic #river https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-00261-6

Nitrogen Dropping Cobalt Strike – A Combination of 'Chemical Elements'
The Nitrogen ransomware group has expanded its operations from North America to Africa and Europe since September 2024. They utilize malvertising tactics, disguising malicious payloads as legitimate software like WinSCP. The group employs DLL sideloading for initial access, followed by Cobalt Strike for lateral movement and post-exploitation activities. The analysis reveals their use of a compromised host as a pivot system and attempts to cover tracks by clearing Windows logs. The investigation uncovered Cobalt Strike configurations through pattern analysis, byte-level XOR decryption, and custom YARA rules. Crash dump analysis using Windows Error Reporting artifacts and WinDBG proved crucial in identifying in-memory indicators of Cobalt Strike beacons and related structures.
Pulse ID: 68152a24acebea26273bad51
Pulse Link: https://otx.alienvault.com/pulse/68152a24acebea26273bad51
Pulse Author: AlienVault
Created: 2025-05-02 20:25:08
Be advised, this data is unverified and should be considered preliminary. Always do further verification.

The answer to that age-old question - where do fish go to #pee?
Scientists make incredible breakthrough after studying #whale urine: 'We soon realized that was only part of the story' https://buff.ly/h16nXar

Hackaday Links: April 27, 2025 - Looks like the Simpsons had it right again, now that an Australian radio station h... - https://hackaday.com/2025/04/27/hackaday-links-april-27-2025/ #anti-submarinewarfare #nitrogen-vacancy #hackadaycolumns #tecxt-to-speech #hackadaylinks #magnetomoter #radiostation #dexterity #hooverdam #deepfake #humanoid #quantum #robot #llm #ai #dj

Hackaday Links: April 27, 2025 https://hackaday.com/2025/04/27/hackaday-links-april-27-2025/ #anti-submarinewarfare #nitrogen-vacancy #HackadayColumns #tecxt-to-speech #Hackadaylinks #hackadaylinks #magnetomoter #radiostation #dexterity #HooverDam #Deepfake #humanoid #quantum #robot #LLM #ai #dj

Netherlands delays nitrogen emissions target, defying its own judges and the EU
The Netherlands is rolling back its nitrogen reduction targets, setting the stage for a showdown with its own judges and Brussels over one of Europe’s most contentious environmental issues
https://www.politico.eu/article/netherlands-delays-nitrogen-emissions-target-defying-own-judges-eu/

[NITROGEN] - Ransomware Victim: Seneca Gaming & Entertainment - https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/nitrogen-ransomware-victim-seneca-gaming-entertainment/
![[NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: Seneca Gaming & Entertainment [NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: Seneca Gaming & Entertainment](https://cdn.fosstodon.org/cache/preview_cards/images/048/174/310/original/bb9e025f0a1c4949.png)
[NITROGEN] - Ransomware Victim: M'AR De AR Hotels - https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/nitrogen-ransomware-victim-m-ar-de-ar-hotels/
![[NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: M’AR De AR Hotels [NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: M’AR De AR Hotels](https://cdn.fosstodon.org/cache/preview_cards/images/048/159/537/original/2aa4f4431ff11c8b.png)
The Netherlands delays its nitrogen emissions target, defying its own judges and the EU.
The Dutch government confirmed it will push back its deadline to halve nitrogen emissions from 2030 to 2035, defying a recent court order.
With its high-density farming, the Netherlands has long been ground zero for Europe’s nitrogen crisis. The country ranks among the EU's worst for nitrogen pollution per hectare.

New post from #Nitrogen : Stadtwerke Schwerte Gmbh
More at : https://www.ransomlook.io/group/Nitrogen #Ransomware
New post from #Nitrogen : M'Ar De Ar Hotels
More at : https://www.ransomlook.io/group/Nitrogen #Ransomware
Did you know some metamorphic #rocks, called metabasic rocks, are an enormous source of #nitrogen being carried deep into the Earth through subduction? A deep nitrogen (N) cycling study by Ananya Mallik, Anna Rebaza, Paul Kapp, Long Li, Yifan Du, Ahmed Al Shams, Emily Cooperdock unveiled these and more. Check out their dataset and article at https://doi.org/10.25422/azu.data.23504415 and https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2023.10.007. Image: Stockcake #OpenData #OpenScience #Geosciences #UniversityofArizona
New post from #Nitrogen : Global Media Group
More at : https://www.ransomlook.io/group/Nitrogen #Ransomware
[NITROGEN] - Ransomware Victim: Global Media Group - https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/nitrogen-ransomware-victim-global-media-group/
![[NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: Global Media Group [NITROGEN] – Ransomware Victim: Global Media Group](https://cdn.fosstodon.org/cache/preview_cards/images/047/798/269/original/1bcc52426bf8d176.png)
#Whale pee moves vital nutrients thousands of miles
'We often think of plants as the lungs of the planet. Animals are the circulatory system.’
Some new research found that great #whales—including right whales, gray whales, and humpbacks—transport roughly 4,000 tons of #nitrogen to low-nutrient coastal areas in the tropics and subtropics every single year. Described as the “great whale pee funnel.”
https://www.popsci.com/environment/whale-pee-nutrients/




